

As its name shows it, this theory is based on Darwinian theory, but adds to it new genetic knowledge. This knowledge allows notably to resolve the problem of characterisation transmission, to which Darwin hadn't brought an answer. This theory uses the idea of species (speciation) but also genetic mutations. Several kinds of genetic mutations exist, that change more or less the genome of the considered specie. Some changes led to the appearance of new alleles (different versions of a pre-existing gene), others to the creation of new genes. So multi-genes families appear, composed of genes very similar in their nucleotides sequence It is supposed their origin is a far ancestral gene, that has undergone mutations.
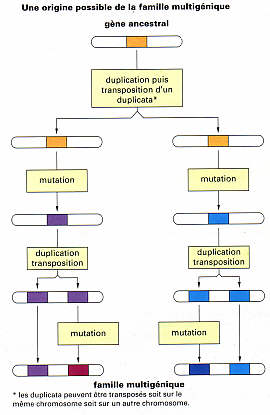
Two phenomenons are the causes for these families creation. The duplication-transposition of genes, and the recombination of part of genes. The first cause appears when a gene is duplicated and transposed on a new locus, different from the original one. The copy of the original gene can also undergo duplication-transposition,. We can observe the emergence of different genes, coding different molecules, but having a common origin. The second phenomenon is based on the existence of a similar part among different molecules. There are interpreted as the result of several duplication of an unique ancestral gene for one of these similitudes of about hundred amino acids. The variable number of similar parts between proteins can be explained if we admit that genes coding these proteins are the result of the recombination of different duplications of the original version of the gene. New genes are so created by associating several gene fragments. These recombinations allow an important intermingling of the genome and seem to have played an important role in Evolution. Today, we discover more of these genes each day. Thanks to these mechanisms, genome shows the high flexibility in evolution needs. But the respect of two conditions is absolutely necessary to the transmission of these mutations:
But "architect genes" (HOM for vertebrate and HOX for invertebrate), which role is to define individual organisation,also have to be mentioned. Mutation of these genes can lead to important physiologic and physiognomic changes. That's why these mutations are very rare, because they are often lethal. Therefore, these genes keep a great importance on Evolution. So all these different phenomenons change the genome of the species, having an influence on its evolution.
Here, Neo-Darwinism hands over to Natural Selection, the supreme referee. It favours mutation transmission if this mutation confers an advantage in a given environment. Indeed, during the same period, several genotypes coexist. Only the better-adapted individuals will survive, or at least will transmit their genome in more important quantity than individuals without the considered mutation.
This theory, itself in constant evolution because it integers new science datas, is accepted by the most of the science community, because it can explain all the evolutionnary phenomenons in fossils or recent species.
Science and technology at that time
In 1995 à Edward B. Lewis, Christianne Nusslein-Volhard et Eric F. Wieschaus received a medicine Nobel prize for their researches concerning genetic control of embryo developpement



In 2000, the most important part of human genome have been decoded



Science and technology at that time
In 1995 à Edward B. Lewis, Christianne Nusslein-Volhard et Eric F. Wieschaus received a medicine Nobel prize for their researches concerning genetic control of embryo developpement



In 2000, the most important part of human genome have been decoded

